Statistical Natural Language Processing in Radiology Reports
This webpage is created to document and share our progress in Radiology NLP.
Hello
I am a second year Biostatistics PhD student at the University of Washington. I am interested the intersection of categorical and longitudinal data, and issues in high-dimensional space, especially in the context of Electronic Medical Records (EMR). Right now I work with Patrick Heagerty as a Research Assistant on statistical Natural Language Processing (NLP) in radiology text reports.
Translating Bioinformatics to Biostatistics
We like each other, and our work overlap often. However some terms they use, we just don't understand. Here are some commonly used Bioinformatics terms and their equivalent definitions in statistics:
Precision
Positve Predictive Value (PPV)
Recall
Sensitivity
F-score (F1)
weighted average of precision and recall.
Ranges between 0 and 1 with 1 being the best score.
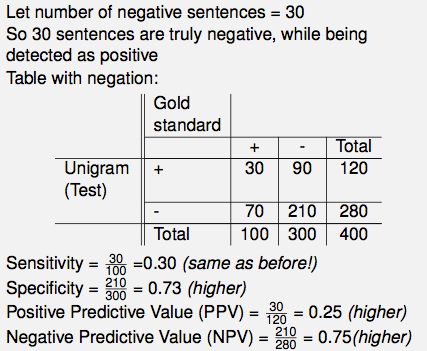
What happens when you say no?
a.k.a. the effect of negation in Error Analysis
This is how a classical 2 by 2 table looks like:
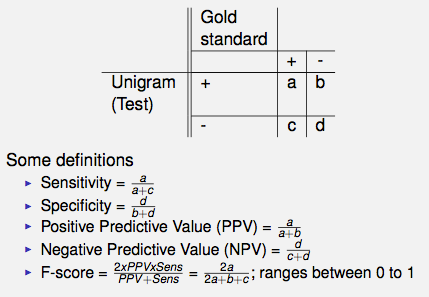
If there is negation, but we don't capture it, here's an example of how our naive perception of a dataset might look like:
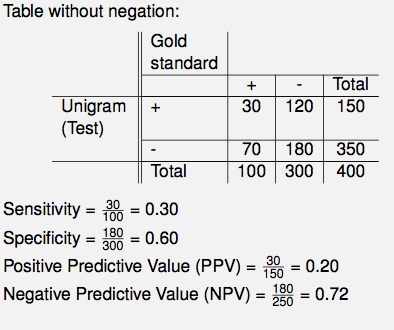
When in reality, this table represents what our dataset REALLY looks like: